What are the structural components of a building
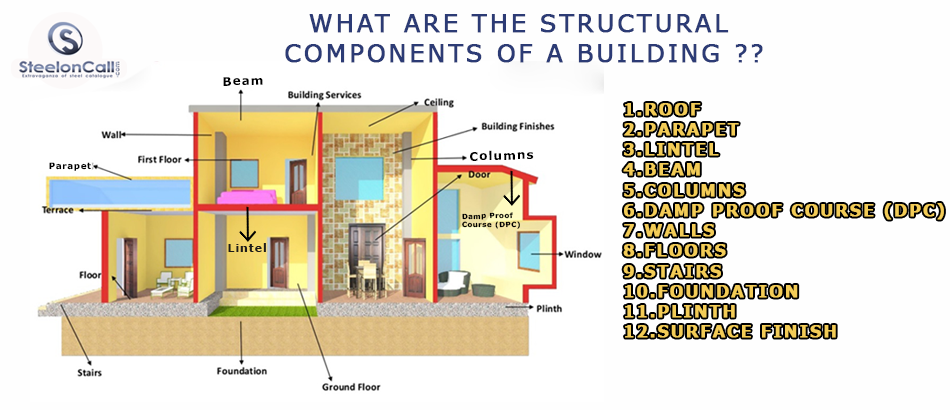
Significantly there are two kinds of structural components present in a structure structure. In that first one is the substructure and the alternate bone is a superstructure. Structure refers to the part of the structure that's constructed below ground position. The abecedarian structure refers to the part of structure above ground position.
Structural factors or superstructures are the primary loads bearing parts of a structure, and each has its veritably own structural parcels, which should be considered. Similar corridor are
- Roof
- Parapet
- Lintel
- Beam
- Columns
- Damp Proof Course (DPC)
- Walls
- Floors
- Stairs
- Foundation
- Plinth
- Surface Finish
Steeloncall is going to explain all types of structural components of a building in a detailed manner.
ROOF:
The rooftop shapes the highest member of a building structure. It covers the top substance of the structure. Rooftops can be either flat or slope dependent on the area and climate states of the region.
PARAPET:
External walls of a structure structure are extended above the rooftop section, known as a alcazar. The sole reason for parapet is to hold water from its passageway into the walls and safety protection for people who use the top of a building structure.
Parapets are of three types, and they're like
1. American Type
2. Reversal Type
3. Cornice Type
LINTEL:
The openings are given in the wall of a structure structure to suit the doors or windows. The factual frame of the door or window is not sufficiently suitable to help the heaviness of the wall over the opening. A different structural element has, in this way, to be presented. It's known as a lintel and is relative to the ray. Climate Tones are generally joined with lintels of windows to shield them from the climate factors, for example, sun, rain, ice.
BEAM:
A plinth ray is constructed, relying on the type of the structure of the structure and the nature of the soil. It gives redundant reliableness concerning agreements of the structure structure and earthquake damages.
COLUMNS:
Columns are perpendicular members constructed above the ground position.
Columns are divided into two types Architectural columns and structural columns. Architectural columns are erected to ameliorate the structure's feel.
The structural column takes the load forming from the arbor over and moves securely to the foundation.
DAMP PROOF COURSE (DPC):
Damp evidence course is a subcaste of waterproofing material, for example, a black-top or waterproof bond. Walls are constructed over the damp evidence course. Damp- evidence route (DPC) avoids face water from thrusting into the walls. Moistness reduces the quality of walls and makes unhealthy living conditions. Likewise, it influences the makeup and plaster and adding the cost of maintenance. Damp proofing subcaste is not needed where a plinth pillar is erected because the plinth ray performs like a DPC.
WALLS:
Walls give the perpendicular enclosure for erecting structures. Bearing walls carry graveness lo acclimate, though shear walls have a significant job in bringing side loads due to wind and earthquakes. Concrete walls erected in the basements of structures structures are exposed to side soil pressure; notwithstanding graveness loads-similar walls are called basement walls.
FLOORS Floors:
are level supporting structural factors of a structure structure. They separate a structure structure into colorful situations to make further convenience on a given plot of land. The essential reason for a bottom is to give a establishment and dry stage for individualities and different effects like outfit, cabinetwork, stores. The position is generally appertained to by its position area.
STAIRS:
A stair is a grouping of way that associates colorful bottoms in a structure structure. The space involved by a stair is called as the stairway. There are different kinds of stairs like a wooden stair, RCC stairs.
FOUNDATION:
The foundations of any structure structure ought to be laid much below the face of the ground, for the below four properties
- To make the steadiness of structure against capsizing due to wind uplift
- To secure an excellent natural bed
- To cover the foundation courses from atmospheric influences
- To drop peril of failure due to agreement of soil
The foundation is the most fundamental part of any structure. Multitudinous bummers are probably due to imperfect foundations rather than any other cause. A good foundation must stay in position without sliding, bowing, disturbing, or bombing in some other way. To accomplish this, the architect must insure that the superstructure, foundation, and soil act together.
PLINTH:
The member of the structure between the face of the girding ground and surface of the bottom, snappily over the earth known as a plinth. The degree of the girding soil is known as arrangement position or ground position. The degree of the ground bottom of the structure structure is known as a plinth position.
SURFACE FINISH:
Surface is one of the significant rudiments that control disunion and transfer subcaste conformation during sliding. Have been made to consider the impact of face texture on disharmony and wear during sliding conditions. Face textures can be anisotropic or isotropic. Occasionally, stick-slip disunion marvels can be seen during sliding, depending upon face texture. Each assembling procedure (for illustration, the multitudinous feathers of machining) produces a face texture. The system is generally upgraded to guarantee that the performing composition isusable.However, a particular procedure will be added to change the original balance, If necessary.
Structural or Superstructure structure factors are specialized architectural structure products planned, designed, and manufactured under controlled conditions for a particular operation. A abecedarian structure part manufacturer or stilt manufacturer is an individual or association constantly enthralled with the manufacturing of factors.

